Female Genital Mutilation (FGM) is a procedure where the female genital organs (vulva) are deliberately cut or injured when there is no medical reason for this to be done.
What are the other names for FGM?
FGM is also called female circumcision, cutting or by other terms such as Sunna, Gudniin, Halalays, Tahoor, Bondo, Ibi.
FGM is illegal
FGM is illegal in the UK. It is child abuse and must never be carried out either here or abroad.
It is illegal to allow or arrange for a child to be taken abroad for FGM procedures or help someone carry out FGM in any way. If caught, offenders face a large fine and a prison sentence of up to 14 years.
If you are worried about someone who is at risk of FGM you must share this information with social services or the police. It is then their responsibility to investigate and protect any girls or women involved.
If someone under the age of 18 has already had FGM this must be reported.
If you are worried that you may be pressured by your family or community to have FGM, or if you are concerned about any girl who may be at risk of FGM, tell a health professional or contact the National Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Children (NSPCC) helpline on 0800 028 3550, 24 hours a day.
The NSPCC can be contacted anonymously or by email fgmhelp@nspcc.org.uk or contact ChildLine on 0800 1111 (Freephone).
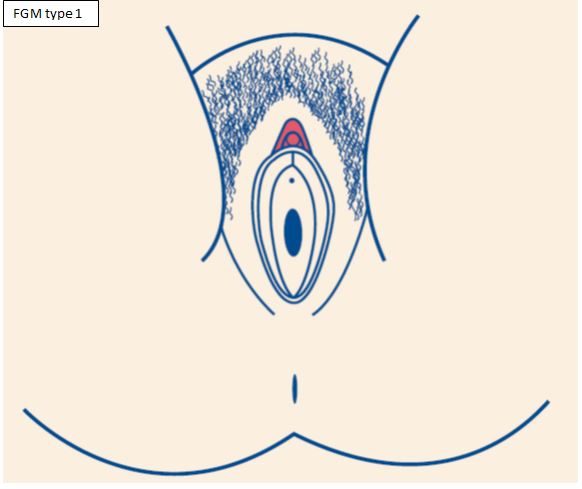
What are the different types of FGM?
There are four different types of FGM.
- Type 1: Removing a part or all of the clitoris
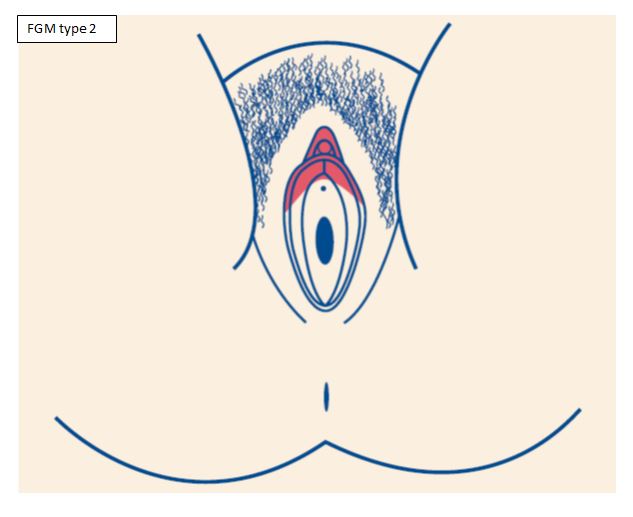
- Type 2: Removing a part or all of the clitoris and the inner labia (lips that surround the vagina), with or without removal of the labia majora (larger outer lips)
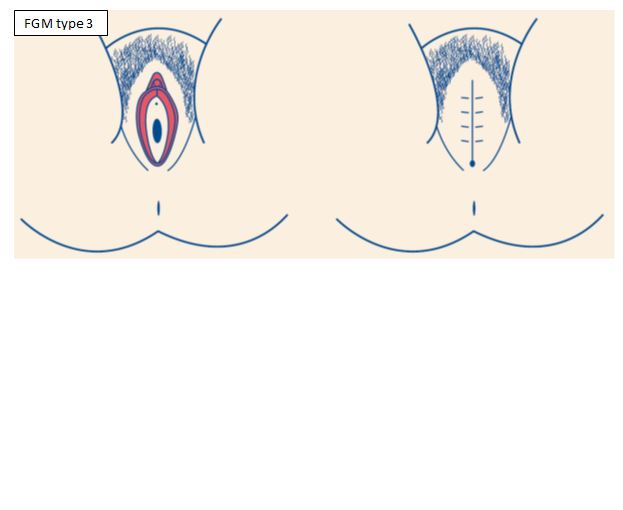
- Type 3: Narrowing of the vaginal opening by creating a seal, formed by cutting and repositioning the labia
- Type 4: All other harmful procedures to the female genitals for non-medical reasons, which include pricking, piercing, cutting, scraping and burning the area
Facts about FGM
FGM is often performed by traditional circumcisers or cutters who do not have any medical training. However, in some countries it may be done by a medical professional.
FGM often happens against a girl’s will without her consent and girls may have to be forcibly restrained.
FGM creates many problems and can cause serious harm.
- Short term complications- haemorrhage, shock, infection
- Long term complications- recurrent urinary and vaginal infections, pain during intercourse, complications during child birth such as bleeding and obstructed labour.
- It may cause depression, flashbacks and self-harm.
Where can I find further information on FGM?
You can get help and support from any healthcare professional. You can also find details of specialist clinics that see and treat women who have had FGM a the following websites:

